apply_matrix()#
Multiplies the current matrix by the one specified through the parameters.
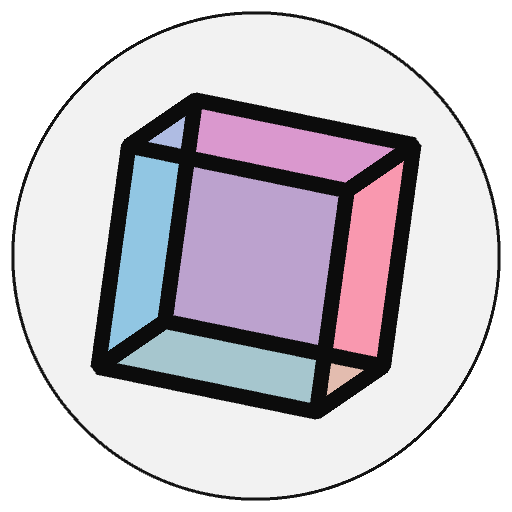
Examples#

def setup():
py5.size(100, 100, py5.P3D)
py5.no_fill()
py5.translate(50, 50, 0)
py5.rotate_y(py5.PI/6)
py5.stroke(153)
py5.box(35)
# set rotation angles
ct = py5.cos(py5.PI/9.0)
st = py5.sin(py5.PI/9.0)
# matrix for rotation around the Y axis
py5.apply_matrix(ct, 0.0, st, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0,
-st, 0.0, ct, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
py5.stroke(255)
py5.box(50)
Description#
Multiplies the current matrix by the one specified through the parameters. This is very slow because it will try to calculate the inverse of the transform, so avoid it whenever possible. The equivalent function in OpenGL is gl_mult_matrix().
Underlying Processing method: applyMatrix
Signatures#
apply_matrix(
n00: float, # numeric value in row 0 and column 0 of the matrix
n01: float, # numeric value in row 0 and column 1 of the matrix
n02: float, # numeric value in row 0 and column 2 of the matrix
n03: float, # numeric value in row 0 and column 3 of the matrix
n10: float, # numeric value in row 1 and column 0 of the matrix
n11: float, # numeric value in row 1 and column 1 of the matrix
n12: float, # numeric value in row 1 and column 2 of the matrix
n13: float, # numeric value in row 1 and column 3 of the matrix
n20: float, # numeric value in row 2 and column 0 of the matrix
n21: float, # numeric value in row 2 and column 1 of the matrix
n22: float, # numeric value in row 2 and column 2 of the matrix
n23: float, # numeric value in row 2 and column 3 of the matrix
n30: float, # numeric value in row 3 and column 0 of the matrix
n31: float, # numeric value in row 3 and column 1 of the matrix
n32: float, # numeric value in row 3 and column 2 of the matrix
n33: float, # numeric value in row 3 and column 3 of the matrix
/,
) -> None
apply_matrix(
n00: float, # numeric value in row 0 and column 0 of the matrix
n01: float, # numeric value in row 0 and column 1 of the matrix
n02: float, # numeric value in row 0 and column 2 of the matrix
n10: float, # numeric value in row 1 and column 0 of the matrix
n11: float, # numeric value in row 1 and column 1 of the matrix
n12: float, # numeric value in row 1 and column 2 of the matrix
/,
) -> None
apply_matrix(
source: npt.NDArray[np.floating], # transformation matrix with a shape of 2x3 for 2D transforms or 4x4 for 3D transforms
/,
) -> None
Updated on March 06, 2023 02:49:26am UTC