Py5Vector.cross()#
Calculate the vector cross product of two 3D vectors.
Examples#
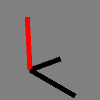
def setup():
py5.size(100, 100, py5.P3D)
py5.background(128)
py5.translate(30, 70)
py5.scale(50)
py5.stroke_weight(0.1)
v1 = py5.Py5Vector(0.7, -0.15, -0.7)
v2 = py5.Py5Vector(0.7, 0.15, 0.7)
py5.line(0, 0, 0, v1.x, v1.y, v1.z)
py5.line(0, 0, 0, v2.x, v2.y, v2.z)
py5.stroke(255, 0, 0)
v3 = v1.cross(v2)
py5.line(0, 0, 0, v3.x, v3.y, v3.z)
Description#
Calculate the vector cross product of two 3D vectors. If one of the vectors is a 2D vector, its z-value is assumed to be zero and the vector cross product is calculated normally. If both vectors are 2D vectors, the returned value will be the wedge product.
Signatures#
cross(
other: Union[Py5Vector, np.ndarray] # 2D or 3D vector to calculate the cross product with
) -> Union[float, Py5Vector, np.ndarray[np.floating]]
Updated on March 06, 2023 02:49:26am UTC